Custom operators
ONNX Runtimeは、公式のONNX演算子ではないカスタム演算子を実行するオプションを提供します。カスタム演算子は、ORTに直接組み込まれた選択された非公式ONNX演算子であるcontrib opsとは異なることに注意してください。
カスタム演算子の定義と登録
Section titled “カスタム演算子の定義と登録”onnxruntime 1.16以降、カスタム演算子は単純に関数として実装できます:
void KernelOne(const Ort::Custom::Tensor<float>& X, const Ort::Custom::Tensor<float>& Y, Ort::Custom::Tensor<float>& Z) { auto input_shape = X.Shape(); auto x_raw = X.Data(); auto y_raw = Y.Data(); auto z_raw = Z.Allocate(input_shape); for (int64_t i = 0; i < Z.NumberOfElement(); ++i) { z_raw[i] = x_raw[i] + y_raw[i]; }}
int main() { Ort::CustomOpDomain v1_domain{"v1"}; // please make sure that custom_op_one has the same lifetime as the consuming session std::unique_ptr<OrtLiteCustomOp> custom_op_one{Ort::Custom::CreateLiteCustomOp("CustomOpOne", "CPUExecutionProvider", KernelOne)}; v1_domain.Add(custom_op_one.get()); Ort::SessionOptions session_options; session_options.Add(v1_domain); // create a session with the session_options ...}属性を持つカスタム演算子の場合、構造体もサポートされています:
struct Merge { Merge(const OrtApi* ort_api, const OrtKernelInfo* info) { int64_t reverse; ORT_ENFORCE(ort_api->KernelInfoGetAttribute_int64(info, "reverse", &reverse) == nullptr); reverse_ = reverse != 0; } // a "Compute" member function is required to be present void Compute(const Ort::Custom::Tensor<std::string_view>& strings_in, std::string_view string_in, Ort::Custom::Tensor<std::string>* strings_out) { std::vector<std::string> string_pool; for (const auto& s : strings_in.Data()) { string_pool.emplace_back(s.data(), s.size()); } string_pool.emplace_back(string_in.data(), string_in.size()); if (reverse_) { for (auto& str : string_pool) { std::reverse(str.begin(), str.end()); } std::reverse(string_pool.begin(), string_pool.end()); } strings_out->SetStringOutput(string_pool, {static_cast<int64_t>(string_pool.size())}); } bool reverse_ = false;};
int main() { Ort::CustomOpDomain v2_domain{"v2"}; // please make sure that mrg_op_ptr has the same lifetime as the consuming session std::unique_ptr<Ort::Custom::OrtLiteCustomOp> mrg_op_ptr{Ort::Custom::CreateLiteCustomOp<Merge>("Merge", "CPUExecutionProvider")}; v2_domain.Add(mrg_op_ptr.get()); Ort::SessionOptions session_options; session_options.Add(v2_domain); // create a session with the session_options ...}構造体がカスタム演算子として実行されるには、“Compute”メンバー関数が必要です。
両方の場合において:
- 入力はconst参照として宣言する必要があります。
- 出力は非const参照として宣言する必要があります。
- Ort::Custom::Tensor::Shape()は入力形状を返します。
- Ort::Custom::Tensor::Data()は生の入力データを返します。
- Ort::Custom::Tensor::NumberOfElement()は入力の要素数を返します。
- Ort::Custom::Tensor::Allocate(…)は出力を割り当て、生データアドレスを返します。
- サポートされているテンプレート引数は:int8_t、int16_t、int32_t、int64_t、float、doubleです。
- 入力としてstd::string_view、出力としてstd::stringをサポートしています。使用方法はこちらを参照してください。
- CPUExecutionProvider上で実行されるカスタム演算子関数の場合、入力としてspanとスカラーがサポートされています。使用方法はこちらを参照してください。
- カーネルコンテキストを期待するカスタム演算子関数については、こちらの例を参照してください。
- unique_ptrを使用して作成されたカスタム演算子をホストする場合は、消費セッションと共に生存させることを確認してください。
カスタム演算子開発と登録のレガシー方法
Section titled “カスタム演算子開発と登録のレガシー方法”カスタム演算子を開発するレガシー方法はまだサポートされています。こちらの例を参照してください。
カスタム演算子ライブラリの作成
Section titled “カスタム演算子ライブラリの作成”カスタム演算子は、別の共有ライブラリ(例:Windowsの.dllやLinuxの.so)で定義できます。カスタム演算子ライブラリはRegisterCustomOps関数をエクスポートし、実装する必要があります。RegisterCustomOps関数は、ライブラリのカスタム演算子を含むOrt::CustomOpDomainを提供されたセッションオプションに追加します。
こちらのプロジェクトとこちらの関連cmakeコマンドを参照してください。
カスタム演算子からネイティブ演算子の呼び出し
Section titled “カスタム演算子からネイティブ演算子の呼び出し”カスタム演算子の実装を簡素化するため、ネイティブonnxruntime演算子を直接呼び出すことができます。例えば、一部のカスタム演算子は他の計算の間にGEMMやTopKを実行する必要があるかもしれません。 これは、状態管理の目的でConvなどのノードの前処理や後処理にも有用です。これを達成するために、ConvノードをCustomConvなどのカスタム演算子でラップし、その中で入力と出力をキャッシュして処理することができます。
この機能はONNX Runtime 1.12.0以降でサポートされています。APIと例を参照してください。
CUDAとROCM用のカスタム演算子
Section titled “CUDAとROCM用のカスタム演算子”onnxruntime 1.16以降、CUDAとROCMデバイス用のカスタム演算子がサポートされています。 デバイス関連のリソースは、デバイス関連のコンテキストを介して演算子内から直接アクセスできます。 CUDAを例に取ると:
void KernelOne(const Ort::Custom::CudaContext& cuda_ctx, const Ort::Custom::Tensor<float>& X, const Ort::Custom::Tensor<float>& Y, Ort::Custom::Tensor<float>& Z) { auto input_shape = X.Shape(); CUSTOM_ENFORCE(cuda_ctx.cuda_stream, "failed to fetch cuda stream"); CUSTOM_ENFORCE(cuda_ctx.cudnn_handle, "failed to fetch cudnn handle"); CUSTOM_ENFORCE(cuda_ctx.cublas_handle, "failed to fetch cublas handle"); auto z_raw = Z.Allocate(input_shape); cuda_add(Z.NumberOfElement(), z_raw, X.Data(), Y.Data(), cuda_ctx.cuda_stream); // launch a kernel inside}完全な例はこちらで見つけることができます。開発をさらに促進するため、CudaContextを介して多様なcuda epリソースと設定が公開されています。詳細についてはヘッダーを参照してください。
ROCMの場合は次のようになります:
void KernelOne(const Ort::Custom::RocmContext& rocm_ctx, const Ort::Custom::Tensor<float>& X, const Ort::Custom::Tensor<float>& Y, Ort::Custom::Tensor<float>& Z) { auto input_shape = X.Shape(); CUSTOM_ENFORCE(rocm_ctx.hip_stream, "failed to fetch hip stream"); CUSTOM_ENFORCE(rocm_ctx.miopen_handle, "failed to fetch miopen handle"); CUSTOM_ENFORCE(rocm_ctx.rblas_handle, "failed to fetch rocblas handle"); auto z_raw = Z.Allocate(input_shape); rocm_add(Z.NumberOfElement(), z_raw, X.Data(), Y.Data(), rocm_ctx.hip_stream); // launch a kernel inside}詳細はこちらで見つけることができます。
1つの演算子、複数の型
Section titled “1つの演算子、複数の型”onnxruntime 1.16以降、カスタム演算子は複数のデータ型をサポートできます:
template <typename T>void MulTop(const Ort::Custom::Span<T>& in, Ort::Custom::Tensor<T>& out) { out.Allocate({1})[0] = in[0] * in[1];}
int main() { std::unique_ptr<OrtLiteCustomOp> c_MulTopOpFloat{Ort::Custom::CreateLiteCustomOp("MulTop", "CPUExecutionProvider", MulTop<float>)}; std::unique_ptr<OrtLiteCustomOp> c_MulTopOpInt32{Ort::Custom::CreateLiteCustomOp("MulTop", "CPUExecutionProvider", MulTop<int32_t>)}; // create a domain adding both c_MulTopOpFloat and c_MulTopOpInt32}コードはこちらで見つけることができます。 ユニットテストケースはこちらで見つけることができます。
カスタム演算子での外部推論ランタイムのラッピング
Section titled “カスタム演算子での外部推論ランタイムのラッピング”カスタム演算子は、外部APIまたはランタイムで推論されるモデル全体をラップすることができます。これにより、外部推論エンジンやAPIとONNX Runtimeの統合を促進できます。
例として、“OpenVINO_Wrapper”という名前のカスタム演算子を持つ次のONNXモデルを考えてみましょう。“OpenVINO_Wrapper”ノードは、OpenVINOのネイティブモデル形式(XMLとBINデータ)でMNISTモデル全体をカプセル化しています。モデルデータはノードの属性にシリアライズされ、後でカスタム演算子のカーネルによって取得され、モデルのメモリ内表現を構築し、OpenVINO C++ APIで推論を実行します。
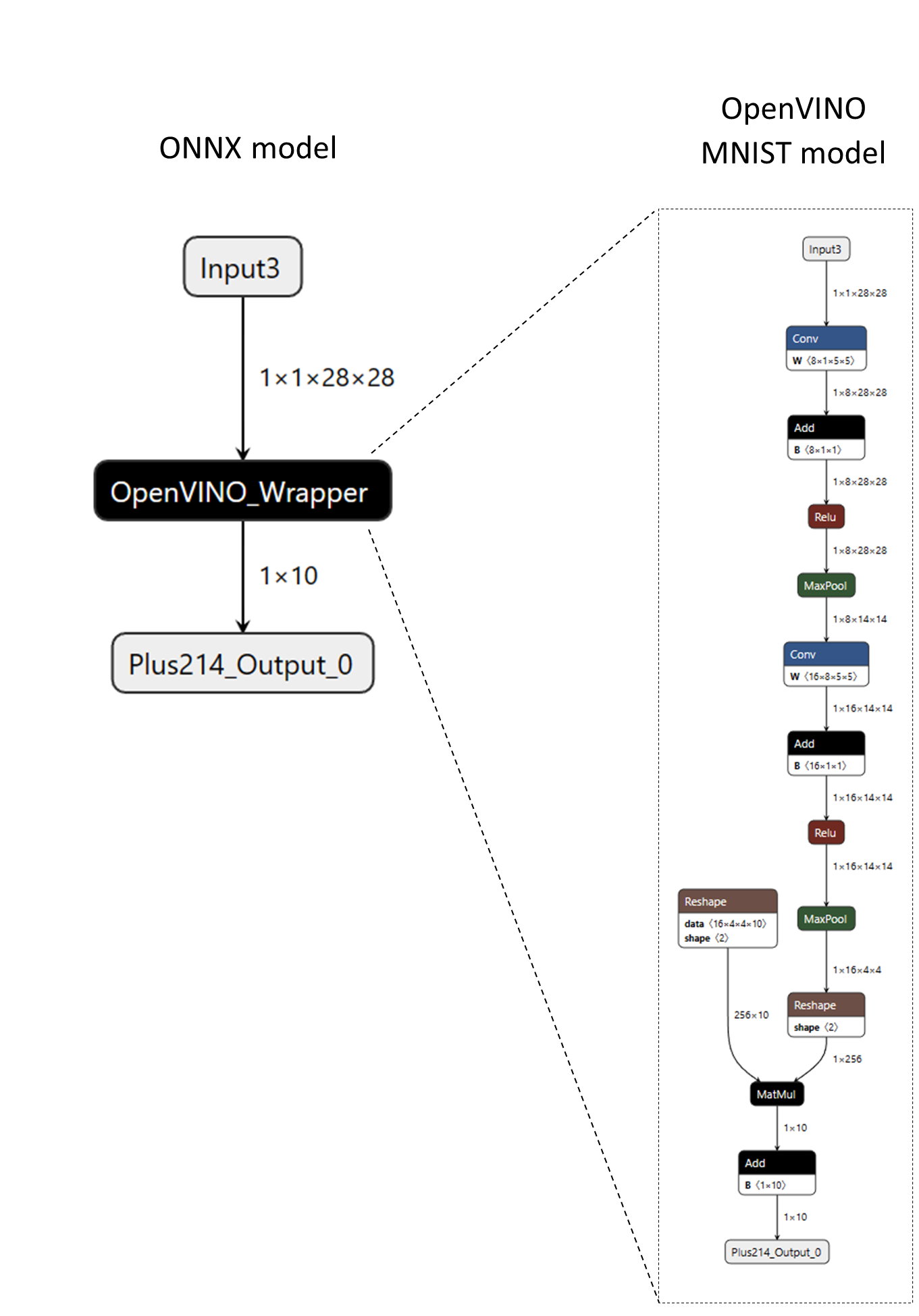
次のコードスニペットは、カスタム演算子の定義方法を示しています。
// Note - below code utilizes legacy custom op interfacesstruct CustomOpOpenVINO : Ort::CustomOpBase<CustomOpOpenVINO, KernelOpenVINO> { explicit CustomOpOpenVINO(Ort::ConstSessionOptions session_options);
CustomOpOpenVINO(const CustomOpOpenVINO&) = delete; CustomOpOpenVINO& operator=(const CustomOpOpenVINO&) = delete;
void* CreateKernel(const OrtApi& api, const OrtKernelInfo* info) const;
constexpr const char* GetName() const noexcept { return "OpenVINO_Wrapper"; }
constexpr const char* GetExecutionProviderType() const noexcept { return "CPUExecutionProvider"; }
// IMPORTANT: In order to wrap a generic runtime-specific model, the custom operator // must have a single non-homogeneous variadic input and output.
constexpr size_t GetInputTypeCount() const noexcept { return 1; }
constexpr size_t GetOutputTypeCount() const noexcept { return 1; }
constexpr ONNXTensorElementDataType GetInputType(size_t /* index */) const noexcept { return ONNX_TENSOR_ELEMENT_DATA_TYPE_UNDEFINED; }
constexpr ONNXTensorElementDataType GetOutputType(size_t /* index */) const noexcept { return ONNX_TENSOR_ELEMENT_DATA_TYPE_UNDEFINED; }
constexpr OrtCustomOpInputOutputCharacteristic GetInputCharacteristic(size_t /* index */) const noexcept { return INPUT_OUTPUT_VARIADIC; }
constexpr OrtCustomOpInputOutputCharacteristic GetOutputCharacteristic(size_t /* index */) const noexcept { return INPUT_OUTPUT_VARIADIC; }
constexpr bool GetVariadicInputHomogeneity() const noexcept { return false; // heterogenous }
constexpr bool GetVariadicOutputHomogeneity() const noexcept { return false; // heterogeneous }
// The "device_type" is configurable at the session level. std::vector<std::string> GetSessionConfigKeys() const { return {"device_type"}; }
private: std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> session_configs_;};カスタム演算子は、単一の可変長/異種入力と単一の可変長/異種出力を持つように定義されていることに注意してください。これは、(MNISTモデルだけでなく)様々な入力と出力の型や形状を持つOpenVINOモデルのラッピングを可能にするために必要です。入力と出力の特性についての詳細は、OrtCustomOp構造体ドキュメントを参照してください。
さらに、カスタム演算子は、アプリケーションによって設定できるセッション設定として”device_type”を宣言しています。次のコードスニペットは、前述のカスタム演算子を含むカスタム演算子ライブラリの登録と設定方法を示しています。
Ort::Env env;Ort::SessionOptions session_options;Ort::CustomOpConfigs custom_op_configs;
// Create local session config entries for the custom op.custom_op_configs.AddConfig("OpenVINO_Wrapper", "device_type", "CPU");
// Register custom op library and pass in the custom op configs (optional).session_options.RegisterCustomOpsLibrary("MyOpenVINOWrapper_Lib.so", custom_op_configs);
Ort::Session session(env, ORT_TSTR("custom_op_mnist_ov_wrapper.onnx"), session_options);詳細については、完全なOpenVINOカスタム演算子ラッパーの例を参照してください。外部モデルや重みをラップするONNXモデルを作成するには、create_custom_op_wrapper.pyツールを参照してください。